Phenomenon-based learning is a learner-centred, multidisciplinary instructional approach that is based on student inquiry and problem solving. The students can get the phenomenon from the real world. For example, to understand and solve a question about climate change, knowledge from different subjects such as science, geography, mathematics, and history may be needed. Students must investigate this phenomenon by asking their own questions, researching facts and providing answers / solutions. Teachers guide them through the process, support steps, and help them with complexity.
What is the phenomenon based learning process like?
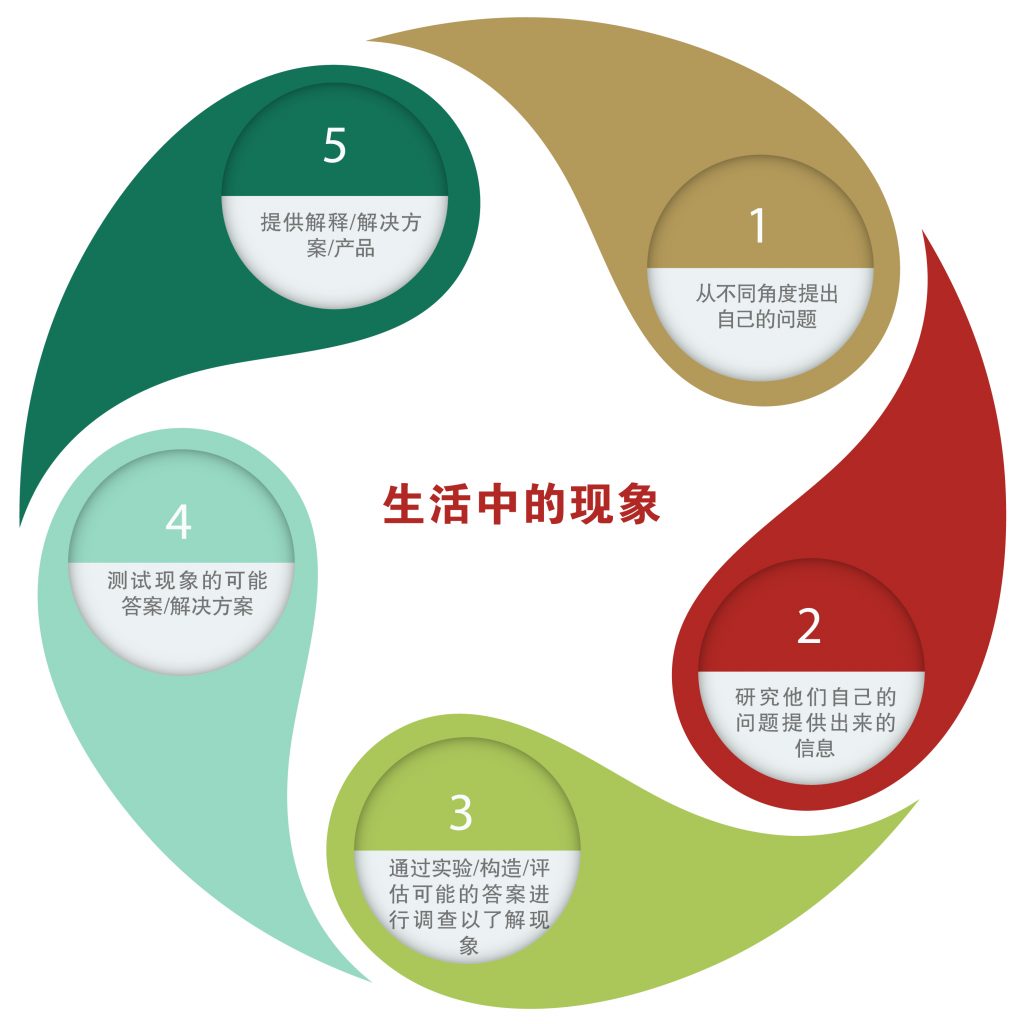
Key Features of Phenomenon Based Learning
- Student Centered: The educator acts as a facilitator and guide, allowing students the freedom to explore the concepts under analysis. The educator does not follow a one size fits all model as each student may be exploring a different problem. PBL is student centered.
- Active Learning: Students learn by ‘doing’ and making connections between concepts in their mind, rather than a passive approach. PBL is an active learning approach.
- Project-based learning: Like ‘project-based learning’ (PBL), PBL also focuses on students learning through projects rather than isolated lessons. Students can focus on a single project for a long period of time to allow immersion, discovery and developing expertise
- Problem-based learning: Students identify problems to solve, determine a range of possible solutions, and implement those solutions to solve the problems. In PBL, the problem is usually related to a specific topic or ‘phenomenon’.
- Social constructivism: Social constructivists embrace the idea that social interactions can help learning to progress. Through social interaction (such as group work), students learn from one another and support each other’s learning.
- Multidisciplinary Learning Modules:The central feature of PBL is its multidisciplinary focus. Rather than teaching subjects in silos, content is taught (and learned) in an integrated manner. Students complete projects that require the application of knowledge from multiple subject areas in order to succeed.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Phenomenon Based Learning
- Students learn how to apply their knowledge to real-world circumstances.
- Students can come to see connections between different domains of learning.
- It emphasizes skills that are required for 21st Century workplaces.
- It highlights the importance of linking theoretical knowledge to practical situations.
- Students get a holistic perspective on the phenomena under analysis.
- Engagement can be enhanced because the focus is on solving problems rather than repetitively doing subject-based tasks.
- Students need to use group work, problem-solving, communication and logical reasoning skills to reach conclusions.
- Students are encouraged to learn in independent cooperative groups to solve large problems.
- Educators across different disciplines can collaborate to create projects for their students.
- Educators can use flexible table layouts rather than traditional classroom layouts to encourage group problem solving.

